NebulaGraph 的云原生 API 网关最佳实践

本文介绍了利用开源 API 网关 APISIX 加速 NebulaGraph 多个场景的落地最佳实践:负载均衡、暴露接口结构与 TLS Termination。
1 API 网关介绍
1.1 什么是 API 网关
API 网关是它位于客户端和服务器之间的“中间人”,用于管理、监控和保护 API。它可以在 API 之前执行一些操作,例如身份验证、授权、缓存、日志记录、审计、流量控制、安全、防火墙、压缩、解压缩、加密、解密等。
API 网关可以工作在 4 层和 7 层。跑在 7 层的API 网关可以使用多种协议,例如 HTTP、HTTPS、WebSocket、gRPC、MQTT 等,在这些应用层协议中做一些操作,例如请求重写、请求转发、请求合并、请求重试、请求缓存、请求限流、请求熔断、请求降级、请求鉴权、请求监控、请求日志、请求审计、请求转发等等。
这里举例一下借助 API 网关可以做的具体的事儿吧:
- 我们可以在网关层增加认证层,比如 JWT 认证、OAuth2 认证、OpenID 认证等等,这样则不需要在每个服务中都做具体的认证集成工作,这可以节省非常多的开发成本。
- 我们可以借助网关给跳板机 SSH 流量增加无需客户端修改的复杂认证,比如跳转任何客户端的 SSH 登录,给出一个网址或者输入框,引导登陆者通过网页的 SSO 认证(包含多因素认证),然后再通过网关转发到 SSH 服务。
- 我们甚至可以在网关层做 Serverless 数据库!TiDB 社区的同学们就在做这个事儿,他们从普通的 MySQL 客户端的登录请求中解析能推断出转到需要的 TiDB 示例的信息,并且在需要 cold start 唤醒实例的时候把连接保持住,可以参考这篇文章:TiDB Gateway。
- 如果我们特别惨在维护一些屎山项目,不得不针对旧版本的应用程序对新版本的服务端进行兼容,这时候 API 网关也可以通过一些请求重写,把旧版本的请求转换成新版本的请求。
只要脑洞大,理论上API 的网关可以做很多很多事儿,显然,不是所有的事情都是适合在这一层面去做的,通常那些比较通用的事情才适合在这一层面去做,这里我只是给出一些典型和极端的具体例子。
1.2 Apache APISIX
API 网关是从 LB、Reverse Proxy 项目演进过来的,随着云原生的兴起,API 网关也逐渐成为了云原生的一部分,流行的开源的网关就有很多:
而且其中很多都是基于 Nginx/OpenResty 的下游项目,这里就以 Apache APISIX 为例,介绍一下 NebulaGraph 借助 API 网关的几个实践。
2 NebulaGraph 介绍
NebulaGraph 是一个开源的分布式图数据库,它的特点是:
- 高性能:NebulaGraph 的性能可以达到每秒百万级的读写,具有极高的扩展性,在千亿点万亿边的规模上支持毫秒级的查询。
- 易扩展:NebulaGraph 的架构是分布式的,可以在多台机器上扩展,每台机器上可以运行多个服务进程,它的查询层是无状态的计算存储分离架构,我们可以很容易引入不同配置、不通类型的计算层,实现同一集群上 TP、AP、 图计算等不同负载的混合查询。
- 易使用:NebulaGraph 的原生查询语言是类 SQL 的,易于学习和使用,同时支持 OpenCypher。
- 丰富生态:NebulaGraph 的生态系统正在不断壮大,目前已经有了多个客户端,包括 Java、Python、Go、C++、JavaScript、Spark、Flink 等,同时也有了多个可视化工具,包括 NebulaGraph Studio、Nebula Dashboard、Nebula Explorer 等。
3 本文讨论的问题
本文给出了基于 NebulaGraph 集群应用中涉及到 API 网关的几个场景。
- 查询接口的负载均衡
- 底层存储接口的暴露
- 传输层的加密
3.1 查询接口负载均衡
首先是图数据库查询接口(GraphD)的负载均衡与高可用的问题。
NebulaGraph 内核由三种服务组成:GraphD、MetaD 和 StorageD:
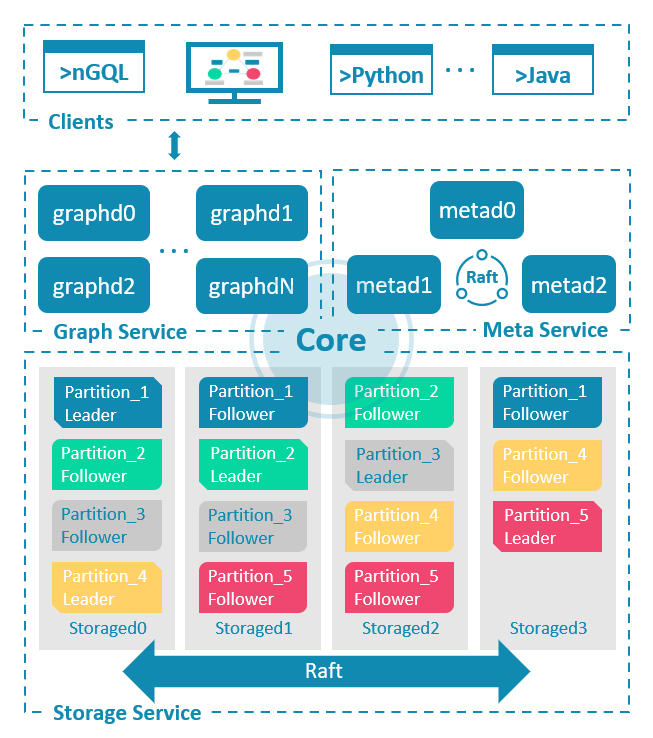
所以,在默认情况下,集群只会暴露 GraphD 的接口,提供给客户端连接,执行 nGQL 的查询。
这其中,GraphD 是无状态的,这意味着我们可以在多个 GraphD 之间做负载均衡。这里,我们有两种方法:基于客户端的(Client-Side LB),与基于代理的。
3.1.1 客户端的负载均衡
客户端的负载均衡,就是在客户端,也就是应用程序中,实现负载均衡的逻辑,NebulaGraph 的各个语言的客户端里边已经内置了简单的轮询(Round-Robin)负载均衡,我们只需要在客户端配置多个 GraphD 的地址就可以了:
比如我们在创建连接池的时候,指定了两个不同的 GraphD 的地址(对应不同进程实例):
from nebula3.gclient.net import ConnectionPool
from nebula3.Config import Config
config = Config()
config.max_connection_pool_size = 10
connection_pool = ConnectionPool()
connection_pool.init([('127.0.0.1', 9669), ('127.0.0.1', 49433)], config)我们在取得连接的时候,就会从连接池中随机取得一个连接:
In [10]: connection0 = connection_pool.get_connection()
In [11]: connection1 = connection_pool.get_connection()
# 这两个连接的 GraphD 地址是不同的
In [12]: connection0._port, connection1._port
Out[12]: (9669, 49433)这种客户端的负载均衡的问题在于它的配置、实现细节与应用代码耦合在一起,如果我们需要修改负载均衡的策略,就需要修改应用代码,这样就会增加应用的复杂度。
3.1.2 代理的负载均衡
基于代理的负载均衡,就是在应用程序之前,增加一个代理层,来实现负载均衡的逻辑,这样应用程序就不需要关心负载均衡的问题了。在 k8s 里的话,我们可以使用 k8s 的 Service 来实现这个代理层。
这是一个在 Minikube 中为 NebulaGraph 集群中 GraphD 创建的 Service:
cat <<EOF | kubectl create -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/cluster: nebula
app.kubernetes.io/component: graphd
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: nebula-operator
app.kubernetes.io/name: nebula-graph
name: nebula-graphd-svc-nodeport
namespace: default
spec:
externalTrafficPolicy: Local
ports:
- name: thrift
port: 9669
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 9669
nodePort: 30000
- name: http
port: 19669
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 19669
nodePort: 30001
selector:
app.kubernetes.io/cluster: nebula
app.kubernetes.io/component: graphd
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: nebula-operator
app.kubernetes.io/name: nebula-graph
type: NodePort
EOF创建了它之后,我们就可以通过它暴露的单独端口来访问 NebulaGraph 集群中的 GraphD 了:
In [13]: connection_pool = ConnectionPool()
...: connection_pool.init([('192.168.49.2', 9669)], config)
Out[13]: True
In [14]: connection0 = connection_pool.get_connection()
In [15]: connection1 = connection_pool.get_connection()
In [16]: connection0._ip, connection1._ip
Out[16]: ('192.168.49.2', '192.168.49.2')可以看到,在连接层面上来看,客户端只知道代理的地址,而不知道 NebulaGraph 集群中的 GraphD 的地址,这样就实现了客户端与 NebulaGraph 集群中的 GraphD 的解耦。
然而,当我们在 connection 之上创建 session 的时候,就能看到实际上客户端的不同请求是落在了不同的 GraphD 上的:
In [17]: session = connection_pool.get_session('root', 'nebula')
In [18]: session._session_id
Out[18]: 1668670607568178
In [19]: session1 = connection_pool.get_session('root', 'nebula')
In [20]: session1._session_id
Out[20]: 1668670625563307
# 得到每一个 session 的 ID
In [21]: session.execute("SHOW SESSIONS")
# 它们分别对应了两个不同的 graphd 实例
Out[21]: ResultSet(keys: ['SessionId', 'UserName', 'SpaceName', 'CreateTime', 'UpdateTime', 'GraphAddr', 'Timezone', 'ClientIp'], values: [1668670607568178, "root", "", utc datetime: 2022-11-17T07:36:47.568178, timezone_offset: 0, utc datetime: 2022-11-17T07:36:47.575303, timezone_offset: 0, "nebula-graphd-0.nebula-graphd-svc.default.svc.cluster.local:9669", 0, "172.17.0.1"],[1668670625563307, "root", "", utc datetime: 2022-11-17T07:37:05.563307, timezone_offset: 0, utc datetime: 2022-11-17T07:37:03.638910, timezone_offset: 0, "nebula-graphd-1.nebula-graphd-svc.default.svc.cluster.local:9669", 0, "172.17.0.1"])3.2 底层存储接口的暴露
在 NebulaGraph 中,我们可以通过 StorageClient 来访问底层的存储接口,这个接口可以用来做一些分析型、数据全扫描计算的工作。
然而存储层的分布式服务实例不像 GraphD 那样,它们是有状态的,这其实与 K8s 或者 Docker Compose 的部署模型是相违背的,如果访问的应用 StorageD 客户端在集群外部,我们需要在 NebulaGraph 集群中的每一个存储实例上都部署一个代理(Service),这非常不方便,有时候还是一种浪费。
此外,由于 NebulaGraph 内部服务发现机制和 StorageD 客户端的实现机制决定,每一个 storaged 服务实体都是由其内部的 host:port 唯一确定和寻址的,这给我们中间的代理工作也带来了一些麻烦。
总结来看,我们的需求是:
- 能够从集群外部访问 NebulaGraph 的存储层每一个实例
- 每一个实例的访问地址(host:port)和内部的地址是完全一致的
为了实现这个需求,我之前的做法是为每一个实例单独部署一个 GraphD 代理(消耗一个地址,保证端口不变),再在外部手动搭一个 nginx 作为代理,配合 DNS 把内部的地址解析 nginx 上,然后通过域名找到上游(每一个单独的 GraphD 代理)。
注:我在这两个 gist 里给出了这个方法的实验步骤:
最近,我找到了一个相对优雅的可维护的方式:
- 在 NebulaGraph 集群同一个命名空间下引入一个 APISIX 网关
- 利用 APISIX 中的 nginx TCP 代理的封装:stream-proxy来暴露 storeaged 的接口
- 为了最终只利用一个集群的出口(Service,我们利用其支持的 TLSv1.3 中的 extend host name 字段:SNI 来路由上游),做到用不同域名的 TCP over TLS 指向后端的不同 storaged
- 最终,只需要 Storage 客户端能支持 TLSv1.3(发送 SNI),并且能解析所有 StorageD 的地址到 APISIX 的 Service 上即可
示例图:
┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ K8s Cluster │
│ ┌──────────────────────────┐ │
│ ┌────────────────────────────────────┐ │ NebulaGraph Cluster │ │
│ │ APISIX API-GATEWAY │ │ ┌──────────────┐ │ │
│ │ │ │ │ Storaged-0 │ │ │
│ │ │ ┌────┼──────▶│ │ │ │
│ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │
│ │ ┌────────────────────────────┐ │ │ │ └──────────────┘ │ │
│ │ │ stream-proxy │ │ │ │ │ │
┌─────┐ │ .─────. │ │ ┌────┐ │ │ │ │ ┌──────────────┐ │ │
│ │ │╱ ╲ │ │ - addr: 9559 │ │──────┼───┼─┘ │ │ Storaged-1 │ │ │
━━┫ DNS ┣━━( Service )╋━━━╋▶ tls: true │ │ │ │ ┌────┼──────▶│ │ │ │
│ │ │`. ,' │ │ │ │──────┼───┼─┘ │ │ │ │ │
└─────┘ │ `───' │ │ │ │ │ │ │ └──────────────┘ │ │
│ │ │ │SNI │ │ │ │ │ │
│ │ │ │ │──────┼───┼─┐ │ ┌──────────────┐ │ │
│ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ Storaged-2 │ │ │
│ │ │ │ │ │ │ └────┼──────▶│ │ │ │
│ │ │ │ │──────┼───┼─┐ │ │ │ │ │
│ │ │ └────┘ │ │ │ │ └──────────────┘ │ │
│ │ └────────────────────────────┘ │ │ │ │ │
│ │ │ │ │ ┌──────────────┐ │ │
│ │ │ │ │ │ Storaged-3 │ │ │
│ │ │ └────┼──────▶│ │ │ │
│ │ │ │ │ │ │ │
│ │ │ │ └──────────────┘ │ │
│ └────────────────────────────────────┘ └──────────────────────────┘ │
│ │
└────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘这样做的好处是:
- 在 APISIX 中比较优雅地维护代理的配置,并且可以用到 APISIX 这些现代化的流量管理能力
- 不需要为每一个 StorageD 单独创建 Service,只需要一个 Service,出集群地址 就可以了
- 为流量增加了 TLSv1.3 的加密,提高了安全性同时没有给 NebulaGraph 集群内部的南北流量带来的性能损耗
在本文的结尾,我会给出一个实操的实验过程,这里包含了本文提到的所有要点和细节。
3.3 传输层的加密
我们在前一个问题中提及到了,在 APISIX 网关中 terminate TLSv1.3 的连接,借助 SNI 信息路由 StorageD 的方法,其实,单独将 GraphD 接口的 TLS 交给网关来做,好处也是非常明显的:
- 证书管理在统一的网关控制面做,更加方便
- 证书运维无 NebulaGraph 集群配置侵入(NebulaGraph 原生支持 TLS 加密,但是加密之后带来了集群内部通信的开销,而且配置和集群其他层面配置在一起,证书更新涉及进程重启,不够灵活)
具体的方法在后边实操中也是有体现的。
4 实操:利用 APISIX 的 stream-proxy 暴露 StorageD 的接口
4.1 实验环境:minikube
我们就在本地的 minikube 上做这个实验吧,首先启动一个 minikube,因为 APISIX 内部的 etcd 需要用到 storageclass,我们带上 穷人版的 storageclass 插件,同时,为了在 k8s 外部访问 storaged 的时候用和内部相同的域名和端口,我们把 node-port 允许的端口扩充到小于 9779 的范围。
minikube start \
--addons="default-storageclass" \
--extra-config=apiserver.service-node-port-range=1-655354.2 实验环境:NebulaGraph on K8s
这里,我们使用 Nebula Operator 来部署 NebulaGraph 集群,具体的部署方法可以参考 Nebula Operator 文档。
咱们做实验,就偷个懒,用我写的 Nebula-Operator-KinD 来一键部署:
curl -sL nebula-kind.siwei.io/install-on-k8s.sh | bash4.3 实验环境:APISIX on k8s
首先是安装,在 Helm 参数中指定打开 stream-proxy 的开关:
helm repo add apisix https://charts.apiseven.com
helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami
helm repo update
helm install apisix apisix/apisix \
--set gateway.type=NodePort \
--set gateway.stream.enabled=true \
--set ingress-controller.enabled=true
# dashboard 也装上,方便我们绕过 admin API call 做一些方便的操作。
helm install apisix-dashboard apisix/apisix-dashboard然后,因为截止到现在,APISIX 的 Helm Chart 之中并没有提供 stream-proxy TCP 的监听端口的 TLS 支持的配置格式,见 https://github.com/apache/apisix-helm-chart/issues/348 ,我们需要手动更改 APISIX 的 configmap,把 stream-proxy 的 TLS 配置加上:
kubectl edit ConfigMap apisix我们编辑把 stream_proxy.tcp 改写成这样:
stream_proxy: # TCP/UDP proxy
only: false
tcp: # TCP proxy port list
- addr: 9779
tls: true
- addr: 9559
tls: true这里我们需要重建 APISIX Pod,因为 APISIX 的 stream-proxy 的 TLS 配置是在启动的时候加载的,所以我们需要重建 APISIX Pod:
kubectl delete $(kubectl get po -l "app.kubernetes.io/name=apisix" -o name)4.4 开始实验
我们看看这个实验的目标,就是把 NebulaGraph 的 StorageD 的接口暴露出来,让外部的客户端可以访问到,而暴露的方式如图:
┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ K8s Cluster │
│ ┌──────────────────────────┐ │
│ ┌────────────────────────────────────┐ │ NebulaGraph Cluster │ │
│ │ APISIX API-GATEWAY │ │ ┌──────────────┐ │ │
│ │ │ │ │ Storaged-0 │ │ │
│ │ │ ┌────┼──────▶│ │ │ │
│ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │
│ │ ┌────────────────────────────┐ │ │ │ └──────────────┘ │ │
│ │ │ stream-proxy │ │ │ │ │ │
┌─────┐ │ .─────. │ │ ┌────┐ │ │ │ │ ┌──────────────┐ │ │
│ │ │╱ ╲ │ │ - addr: 9559 │ │──────┼───┼─┘ │ │ Storaged-1 │ │ │
━━┫ DNS ┣━━( Service )╋━━━╋▶ tls: true │ │ │ │ ┌────┼──────▶│ │ │ │
│ │ │`. ,' │ │ │ │──────┼───┼─┘ │ │ │ │ │
└─────┘ │ `───' │ │ │ │ │ │ │ └──────────────┘ │ │
│ │ │ │SNI │ │ │ │ │ │
│ │ │ │ │──────┼───┼─┐ │ ┌──────────────┐ │ │
│ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ Storaged-2 │ │ │
│ │ │ │ │ │ │ └────┼──────▶│ │ │ │
│ │ │ │ │──────┼───┼─┐ │ │ │ │ │
│ │ │ └────┘ │ │ │ │ └──────────────┘ │ │
│ │ └────────────────────────────┘ │ │ │ │ │
│ │ │ │ │ ┌──────────────┐ │ │
│ │ │ │ │ │ Storaged-3 │ │ │
│ │ │ └────┼──────▶│ │ │ │
│ │ │ │ │ │ │ │
│ │ │ │ └──────────────┘ │ │
│ └────────────────────────────────────┘ └──────────────────────────┘ │
│ │
└────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘我们已经有了所有的框架,我们要往里填箭头和圆圈了。
$ kubectl get po
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
apisix-6d89854bc5-5m788 1/1 Running 1 (31h ago) 2d4h
apisix-dashboard-b544bd766-nh79j 1/1 Running 8 (31h ago) 2d10h
apisix-etcd-0 1/1 Running 2 (31h ago) 2d10h
apisix-etcd-1 1/1 Running 2 (31h ago) 2d10h
apisix-etcd-2 1/1 Running 2 (31h ago) 2d10h
nebula-graphd-0 1/1 Running 2 (31h ago) 3d4h
nebula-metad-0 1/1 Running 2 (31h ago) 3d4h
nebula-storaged-0 1/1 Running 2 (31h ago) 3d4h
nebula-storaged-1 1/1 Running 2 (31h ago) 3d4h
nebula-storaged-2 1/1 Running 2 (31h ago) 3d4h4.4.1 配置 APISIX 的 stream-proxy
参考 APISIX 文档:https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/stream-proxy/#accept-tls-over-tcp-connection
我们用 APISIX 的 API 来配置 stream-proxy:
apisix_api_key="edd1c9f034335f136f87ad84b625c8f1"
apisix_pod=$(kubectl get po -l \
"app.kubernetes.io/name=apisix" -o name)
kubectl exec -it $apisix_pod -- \
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/stream_routes/1 \
-H "X-API-KEY: $apisix_api_key" -X PUT -d \
'{
"sni": "nebula-storaged-0.nebula-storaged-headless.default.svc.cluster.local",
"upstream": {
"nodes": {
"172.17.0.13:9779": 1
},
"type": "roundrobin"
}
}'
kubectl exec -it $apisix_pod -- \
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/stream_routes/2 \
-H "X-API-KEY: $apisix_api_key" -X PUT -d \
'{
"sni": "nebula-storaged-1.nebula-storaged-headless.default.svc.cluster.local",
"upstream": {
"nodes": {
"172.17.0.18:9779": 1
},
"type": "roundrobin"
}
}'
kubectl exec -it $apisix_pod -- \
curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/stream_routes/3 \
-H "X-API-KEY: $apisix_api_key" -X PUT -d \
'{
"sni": "nebula-storaged-2.nebula-storaged-headless.default.svc.cluster.local",
"upstream": {
"nodes": {
"172.17.0.5:9779": 1
},
"type": "roundrobin"
}
}'注意,当下,APISIX 的 stream-proxy 上游节点不支持域名解析,是受限于上游的 lua 库,详见我报的 issue:https://github.com/apache/apisix/issues/8334 ,理想情况下,我们这里应该给出每一个 storaged 的 SNI 相同的地址作为
upstream.nodes,好像:kubectl exec -it $apisix_pod -- \ curl http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/stream_routes/1 \ -H "X-API-KEY: $apisix_api_key" -X PUT -d \ '{ "sni": "nebula-storaged-0.nebula-storaged-headless.default.svc.cluster.local", "upstream": { "nodes": { "nebula-storaged-0.nebula-storaged-headless.default.svc.cluster.local": 1 }, "type": "roundrobin" } }'
4.4.2 配置 APISIX 中 storaged 地址的 TLS 证书
在生产环境下,我们应该云原生的方式去管理自签或者公共信任的证书,这里,我们就手动利用 mkcert 工具来做这件事儿。
安装 mkcert
# 首次运行,需要安装 mkcert,并且生成根证书
# macOS 的话
brew install mkcert
# ubuntu 的话
apt-get install wget libnss3-tools
# 然后再去 https://github.com/FiloSottile/mkcert/releases/ 下载 mkcert签发证书:
mkcert '*.nebula-storaged-headless.default.svc.cluster.local'利用 APISIX-dashboard 将证书导入到 APISIX 之中
单独开一个终端,运行:
export POD_NAME=$(\
kubectl get pods \
-l "app.kubernetes.io/name=apisix-dashboard,app.kubernetes.io/instance=apisix-dashboard" \
-o jsonpath="{.items[0].metadata.name}")
export CONTAINER_PORT=$(\
kubectl get pod $POD_NAME \
-o jsonpath="{.spec.containers[0].ports[0].containerPort}")
kubectl \
port-forward $POD_NAME 8080:$CONTAINER_PORT --address='0.0.0.0'浏览器访问 http://10.1.1.168:8080/ssl/list ,账号密码都是 admin ,点击 Create 按钮,将刚刚生成的证书导入到 APISIX 之中。
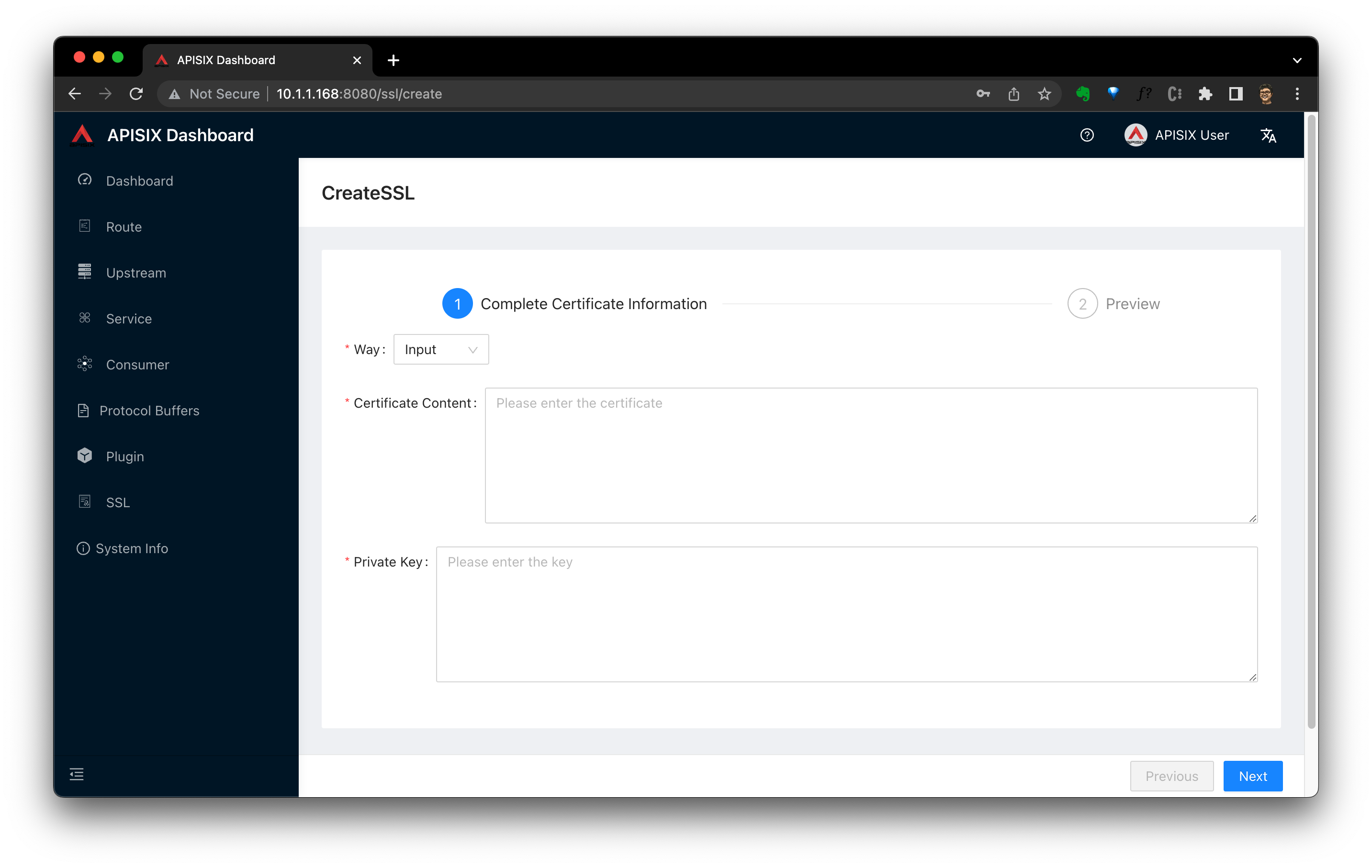
4.4.3 增加 APISIX 的 NodePort Service
创建一个 NodePort Service,用于暴露 APISIX 的 9779 端口,这样,我们就可以通过外部的 IP 地址访问到 APISIX 了。
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
spec:
selector:
app.kubernetes.io/instance: apisix
app.kubernetes.io/name: apisix
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 9779
targetPort: 9779
name: thrift
nodePort: 9779
type: NodePort
EOF因为前边 minikube 中我们配置了端口的范围覆盖到了 9779,所以我们可以看到,这个 NodePort Service 的端口在宿主机上也可以从 minikube ip 的同一个端口访问到:
$ minikube service apisix-svc
$ minikube service list
|------------------------|---------------------------------|-------------------|---------------------------|
| NAMESPACE | NAME | TARGET PORT | URL |
|------------------------|---------------------------------|-------------------|---------------------------|
...
| default | apisix-svc | thrift/9779 | http://192.168.49.2:9779 |<---
...
|------------------------|---------------------------------|-------------------|---------------------------|当然,minikube 假设我们的服务都是 HTTP 的,给出的 URL 是 HTTP:// 的,不用理会它,我们心里知道它是 TCP over TLS 就好了。
4.4.4 配置 K8s 外部 DNS
我们需要配置一个 DNS 服务,让我们可以通过 nebula-storaged-0.nebula-storaged-headless.default.svc.cluster.local 等三个域名通过 minikube 的 NodePort Service 访问到我们的 NebulaGraph 的 storaged 服务。
获得 minikube 的 IP 地址:
$ minikube ip
192.168.49.2配置 /etc/hosts
192.168.49.2 nebula-storaged-0.nebula-storaged-headless.default.svc.cluster.local
192.168.49.2 nebula-storaged-1.nebula-storaged-headless.default.svc.cluster.local
192.168.49.2 nebula-storaged-2.nebula-storaged-headless.default.svc.cluster.local
192.168.49.2 nebula-metad-0.nebula-metad-headless.default.svc.cluster.local4.4.5 验证 NebulaGraph Storage Client 可以从所有的节点中获取到数据
这里,为了方便,我们用到 python 的客户端。
由于在写本文的时候,NebulaGraph Python 客户端的 StorageClient 尚未支持 TLS,对它支持的 PR 刚好是我为了本实验写的:https://github.com/vesoft-inc/nebula-python/pull/239 。
所以我们要从我的个人分支安装这个客户端:
git clone https://github.com/wey-gu/nebula-python.git
cd nebula-python
python3 -m pip install .
python3 -m pip install ipython
# 进入 ipython
ipython我们在 iPython 中交互式验证:
from nebula3.mclient import MetaCache, HostAddr
from nebula3.sclient.GraphStorageClient import GraphStorageClient
from nebula3.Config import SSL_config
import ssl
import os
meta_cache = MetaCache([('nebula-metad-0.nebula-metad-headless.default.svc.cluster.local', 9559)],
50000)
storage_addrs = [HostAddr(host='nebula-storaged-0.nebula-storaged-headless.default.svc.cluster.local', port=9779),
HostAddr(host='nebula-storaged-1.nebula-storaged-headless.default.svc.cluster.local', port=9779),
HostAddr(host='nebula-storaged-2.nebula-storaged-headless.default.svc.cluster.local', port=9779)]
# 自签证书配置
current_dir = os.path.abspath(".")
ssl_config = SSL_config()
ssl_config.cert_reqs = ssl.CERT_OPTIONAL
ssl_config.cert_reqs = ssl.CERT_OPTIONAL
ssl_config.ca_certs = os.path.join(
os.path.expanduser("~/.local/share/mkcert"), 'rootCA.pem'
)
ssl_config.keyfile = os.path.join(
current_dir, 'nebula-storaged-headless.default.svc.cluster.local+1-key.pem'
)
ssl_config.certfile = os.path.join(
current_dir, 'nebula-storaged-headless.default.svc.cluster.local+1.pem'
)
# 实例化 StorageClient
graph_storage_client = GraphStorageClient(meta_cache, storage_addrs, 5000, ssl_config)
# 验证可以从所有的节点中获取到数据
resp = graph_storage_client.scan_vertex(
space_name='basketballplayer',
tag_name='player')
while resp.has_next():
result = resp.next()
for vertex_data in result:
print(vertex_data)结果✅:
("player112" :player{name: "Jonathon Simmons", age: 29})
("player1120" :player{name: "李四", age: 30})
("player117" :player{name: "Stephen Curry", age: 31})
("player119" :player{name: "Kevin Durant", age: 30})
("player134" :player{name: "Blake Griffin", age: 30})
("player141" :player{name: "Ray Allen", age: 43})
("player144" :player{name: "Shaquille O'Neal", age: 47})
("player149" :player{name: "Ben Simmons", age: 22})
("player100" :player{name: "Tim Duncan", age: 42})
("player101" :player{name: "Tony Parker", age: 36})
("player110" :player{name: "Cory Joseph", age: 27})
("player126" :player{name: "Kyrie Irving", age: 26})
("player131" :player{name: "Paul George", age: 28})
("player133" :player{name: "Yao Ming", age: 38})
("player140" :player{name: "Grant Hill", age: 46})
("player105" :player{name: "Danny Green", age: 31})
("player109" :player{name: "Tiago Splitter", age: 34})
("player111" :player{name: "David West", age: 38})
...5 总结
- NebulaGraph 查询接口的负载均衡可以借助 K8s Service来做;
- NebulaGraph 底层存储接口的暴露在 K8s 中可以利用 APISIX Stream Proxy 和 SNI 来优雅实现;
- 利用 API 网关对出口传输层的加密是一个很好的选择,相较于用 NebulaGraph 原生的 TLS 的方式。
6 一些坑
-
发现 fbthrift python 并不支持 发送 extend host name(SNI),https://github.com/vesoft-inc/nebula-python/pull/238 ,写了 PR 去做支持,这时候 APISIX 中的报错是
failed to find SNI:2022/11/15 10:18:26 [error] 78#78: *1744270 stream [lua] init.lua:842: stream_ssl_phase(): failed to fetch ssl config: failed to find SNI: please check if the client requests via IP or uses an outdated protocol. If you need to report an issue, provide a packet capture file of the TLS handshake., context: ssl_certificate_by_lua*, client: 172.17.0.1, server: 0.0.0.0:9779参考:
- https://docs.python.org/3/library/ssl.html#ssl.SSLContext.sslsocket_class
- https://github.com/apache/thrift/commit/937228e030569bf25ceb379c9491426709792701
- https://github.com/apache/thrift/pull/894
- https://github.com/apache/thrift/blob/e8353cb46e9f5e71f9b76f55d6bf59530b7f98ef/lib/py/src/transport/TSSLSocket.py#L184
-
发现 APISIX stream 里边不解析上游 node 域名,我查了所有一溜的 dns 都没有问题,去提了 issue 才知道是已知问题:https://github.com/apache/apisix/issues/8334,只好先手配
IP:Port作罢。2022/11/15 12:26:59 [error] 44#44: *9538531 stream [lua] resolver.lua:47: parse_domain(): failed to parse domain: nebula-storaged-0.nebula-storaged-headless.default.svc.cluster.local, error: failed to query the DNS server: dns client error: 101 empty record received while prereading client data, client: 172.17.0.1, server: 0.0.0.0:9779 2022/11/15 12:26:59 [error] 44#44: *9538531 stream [lua] upstream.lua:79: parse_domain_for_nodes(): dns resolver domain: nebula-storaged-0.nebula-storaged-headless.default.svc.cluster.local error: failed to query the DNS server: dns client error: 101 empty record received while prereading client data, client: 172.17.0.1, server: 0.0.0.0:9779 2022/11/15 12:26:59 [error] 44#44: *9538531 stream [lua] init.lua:965: stream_preread_phase(): failed to set upstream: no valid upstream node while prereading client data, client: 172.17.0.1, server: 0.0.0.0:9779
题图版权 Lars